Transistors BJT explained in details with solved examples Circuit Diagram In order for a transistor to properly function as a current regulator, the controlling (base) current and the controlled (collector) currents must be going in the proper directions: meshing additively at the emitter and going in the direction of the emitter arrow symbol. RELATED WORKSHEET: Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) Theory Worksheet

The BJT Transistor as a Switch. To use a bipolar junction transistor as a switch, use the common emitter configuration: Emitter: Connected to the ground (0V reference). Collector: Connected to the load (e.g., a lamp). Base: Connected to the control signal (e.g., push button, microcontroller). Load: Connected between the collector and the supply
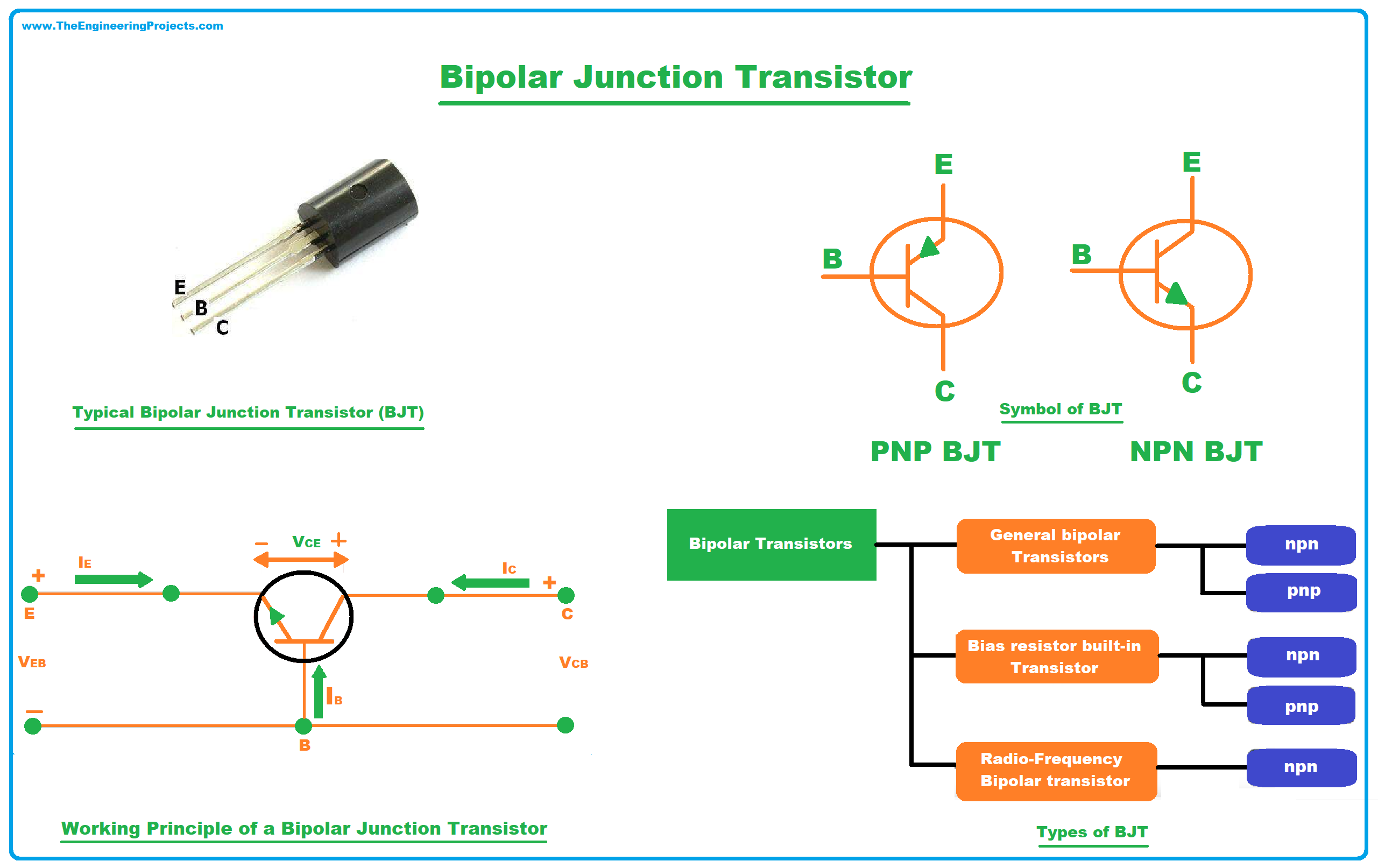
Introduction to Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJT) Circuit Diagram
What is a Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) and how does it work? The transistor is classically defined as a three-terminal semiconductor device that operates as a linear amplifier, oscillator, or digital switch. To intuitively understand transistors, you will need to build a circuit. Start by building the beginner transistor circuits Variability in Current Gain: β can vary widely among transistors of the same type. Saturation Mode: In saturation, R CE approaches zero, causing V CE to be almost zero. Frequently Asked Questions 1. What is the purpose of using a BJT in a circuit? A BJT can act as an amplifier to increase signal power or as a switch to control circuit flow. 2.

device and it comes in two general types: the Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) and the Field Effect Transistor (FET). Here we will describe the system characteristics of the BJT configuration and explore its use in fundamental signal shaping and amplifier circuits. The BJT is a three terminal device and it comes in two different types. The npn

Build Electronic Circuits Circuit Diagram
In the second installment of this series, we will explain Vceo (collector-emitter voltage) and Vces (collector-emitter breakdown voltage).. Collector-emitter voltage Vceo. Vceo is the breakdown voltage when the depletion layer that spreads from the base to the emitter and the depletion layer that spreads from the EB junction to the base collide. (See Figure 5 on the left below)
